Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a lightweight, rigid, and highly versatile material commonly used in packaging, insulation, and construction. Its widespread use can be attributed to its excellent insulating properties and cost-effectiveness. However, one challenge associated with EPS is its disposal and recycling. It is a plastic product, so finding efficient ways to manage waste EPS is critical. One method of dealing with EPS waste involves melting it down for recycling or disposal. But what exactly melts EPS, and how does the process work?
In this article, we will explore how EPS can be melted, what materials or methods cause it to break down, and how technologies like EPS melting machines are helping to tackle the problem of EPS waste.
What is EPS?
EPS is made from polystyrene beads that expand when exposed to heat and steam during manufacturing. The expanded beads are then molded into various shapes, such as packaging materials, insulation boards, and lightweight construction blocks. Due to its structure, EPS is primarily composed of air—up to 98%—making it lightweight and bulky. Its large volume can pose storage and transportation challenges when disposing or recycling EPS waste, which is why melting it down is often seen as a practical solution.
What Melts EPS?
EPS can be melted by exposing it to heat, solvents, or EPS melting machines. Let’s explore each method in detail:
1. Heat
One of the simplest ways to melt EPS is by applying heat. When EPS is exposed to temperatures above its melting point—around 240°F (115°C)—it starts to soften and melt. However, heating EPS directly can release toxic fumes, such as styrene and benzene, which are harmful to both human health and the environment.
Typically, heat-based melting of EPS is done in controlled industrial settings where proper ventilation and emission control systems are in place. In these settings, the melted EPS can be formed into a more compact, dense mass, making it easier to store, transport, and recycle.
2. Solvents
Another method of breaking down or “melting” EPS is by using chemical solvents. Certain organic solvents, like acetone, are capable of dissolving EPS, causing it to collapse into a much smaller volume. While the material does not technically melt in the same way it does with heat, the solvent breaks down the polystyrene’s structure, reducing its bulk.
Acetone and other solvents work by dissolving the bonds between the polystyrene molecules, allowing the trapped air inside the EPS to escape. This method is often used when a quicker solution is needed, especially in small-scale operations. However, using solvents for EPS disposal poses environmental risks, as some solvents can be hazardous and require careful handling.
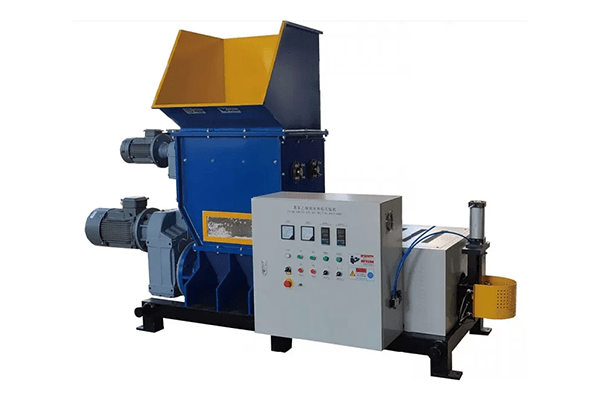
3. EPS Melting Machines
For large-scale recycling and disposal operations, EPS melting machines are one of the most efficient and environmentally friendly solutions. These machines are specifically designed to handle bulky EPS waste by melting it down through a controlled heating process.
EPS melting machines work by feeding the expanded polystyrene into a chamber where it is exposed to heat. As the EPS melts, the machine compacts the material, reducing it by up to 90% of its original volume. The melted EPS is then extruded into dense blocks or ingots, which can be easily transported and repurposed for recycling.
This process offers several advantages:
- Volume Reduction: The bulky EPS is reduced to a fraction of its original size, making it more manageable for storage and transportation.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern EPS melting machines are designed to use energy efficiently, reducing the overall environmental impact of melting large quantities of EPS.
- Recycling Potential: Once melted, the EPS can be reused in various ways. It can be reprocessed into new polystyrene products, used in construction materials, or even repurposed for 3D printing filament.
EPS melting machines are commonly used by industries, recycling centers, and waste management facilities that handle large amounts of EPS waste.
Environmental Considerations
While melting EPS can help address the problem of its bulkiness and make recycling more practical, it is important to note that the process must be conducted responsibly to minimize environmental harm. Improperly heating EPS, especially without adequate ventilation, can release toxic fumes that contribute to air pollution and pose health risks.
Moreover, when using solvents to dissolve EPS, care must be taken to manage the chemicals involved properly. Solvents like acetone can evaporate quickly, releasing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere, which can contribute to air quality degradation if not handled properly.
Conclusion
Melting EPS is a practical solution for reducing its bulk and making it easier to recycle or dispose of. Heat, solvents, and specialized EPS melting machines are all methods that can be used to achieve this. Among these options, EPS melting machines are particularly effective for large-scale operations, offering a cleaner, safer, and more environmentally friendly method of handling EPS waste.
With growing environmental concerns surrounding plastic waste, recycling EPS through melting processes can help reduce landfill usage and offer new opportunities for repurposing the material. As technology continues to evolve, innovative solutions like EPS melting machines will likely play a larger role in tackling the global challenge of managing plastic waste.
Post time: 10-12-2024