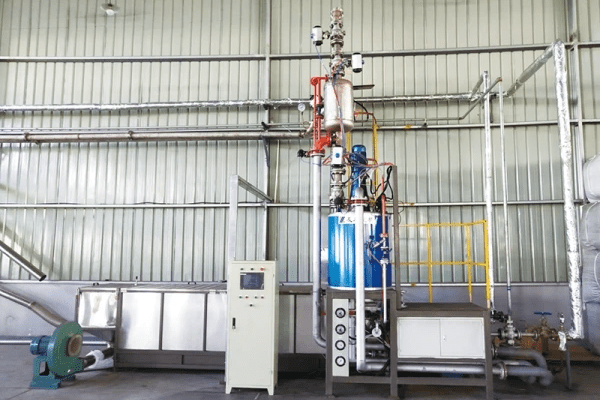
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam is a widely used material known for its lightweight, insulating, and shock-absorbing properties. From packaging and construction to insulation and even in various consumer products, EPS foam plays a crucial role across multiple industries. One of the critical stages in the production of EPS foam is the pre-expansion process, which is essential for achieving the material’s final properties. The continuous EPS pre-expander, a specialized machine used in this process, plays a pivotal role in ensuring the quality and consistency of the final product.
Understanding EPS and the Importance of Pre-Expansion
EPS foam starts as tiny beads of polystyrene resin. These beads, although small, have the potential to expand dramatically when exposed to heat and steam. The pre-expansion process is the first step in converting these raw beads into foam products that are used in various applications.
Pre-expansion is crucial because it sets the foundation for the density, structure, and quality of the final EPS foam product. Without this process, the beads would not expand properly, leading to an inconsistent and low-quality foam that may not meet the required standards for insulation, packaging, or other uses.
The EPS Pre-Expansion Process
The EPS pre-expansion process involves heating the polystyrene beads with steam, causing them to expand and form closed-cell foam structures. The process can be broken down into several key stages:
1. Raw Material Preparation: The process begins with the preparation of raw polystyrene beads. These beads contain a blowing agent, usually pentane, which is responsible for the expansion. The beads are stored in silos or hoppers and are then fed into the pre-expander machine.
2. Heating and Expansion: Once inside the continuous EPS pre-expander, the beads are exposed to steam. The heat causes the blowing agent within the beads to vaporize, creating gas bubbles inside each bead. This expansion process increases the bead size by up to 40 times their original volume, transforming them into lightweight foam particles. The density of the expanded beads can be controlled by adjusting the steam temperature and the duration of the heating process.
3. Stabilization: After the initial expansion, the beads are transferred to a fluidized bed dryer or aging silo where they are allowed to cool and stabilize. During this stage, the beads lose some of the internal pressure created during expansion and reach a state of equilibrium. This stabilization is crucial to ensure that the beads retain their expanded size and shape before they are further processed.
4. Secondary Expansion (Optional): In some cases, a second pre-expansion stage may be required to achieve the desired bead size and density. This secondary expansion can be done using the same continuous EPS pre-expander or a separate machine, depending on the production requirements.
5. Storage and Molding: Once the pre-expanded beads have stabilized, they are stored in aging silos before being molded into the final product. The storage period allows the beads to further stabilize and ensures that they are ready for the next stage of production, where they will be shaped into insulation panels, packaging materials, or other EPS foam products.
The Role of Continuous EPS Pre-Expanders
The continuous EPS pre-expander is a key piece of equipment in the EPS manufacturing process. Unlike batch pre-expanders, which process a set amount of beads at a time, continuous pre-expanders allow for a constant flow of material through the machine. This continuous process offers several advantages:
1. Consistency and Efficiency: Continuous EPS pre-expanders provide a more consistent expansion process, resulting in uniform bead size and density. This consistency is vital for producing high-quality EPS foam products that meet industry standards.
2. Higher Production Capacity: By operating continuously, these machines can handle larger volumes of raw beads, increasing production capacity. This is particularly beneficial for large-scale manufacturing operations where high throughput is required.
3. Reduced Energy Consumption: Continuous EPS pre-expanders are designed to optimize energy use. By maintaining a steady flow of beads through the machine, energy efficiency is improved, reducing overall production costs and environmental impact.
4. Enhanced Control: These machines offer precise control over the expansion process, allowing manufacturers to fine-tune the bead size, density, and other parameters to meet specific requirements. This level of control is crucial for producing EPS foam with the exact properties needed for different applications.
The Future of EPS Pre-Expansion
As the demand for EPS foam continues to grow across various industries, advancements in pre-expansion technology are likely to focus on improving efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and enhancing the quality of the final product. Innovations in continuous EPS pre-expanders, such as automated controls and improved thermal management, are expected to play a significant role in these developments.
Conclusion
The process of EPS pre-expansion is a critical step in the production of expanded polystyrene foam, determining the material’s final properties and quality. The use of continuous EPS pre-expanders has revolutionized this process, offering greater efficiency, consistency, and control over the expansion of polystyrene beads. As technology continues to evolve, these machines will remain essential in meeting the growing demand for high-quality EPS foam across various industries.
Post time: 08-16-2024