Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a lightweight, rigid foam material widely used in the construction and packaging industries. EPS blocks are formed through EPS block molding, which involves expanding polystyrene beads, fusing them, and shaping them into large, dense blocks. These blocks are then used for insulation, packaging, and other applications. The production of these blocks is made possible by specialized machinery, particularly the EPS Block Machine, which plays a critical role in molding.
In this article, we’ll walk through the various stages of the EPS block molding process, highlighting the equipment and steps involved.
1. Pre-Expansion
The first step in the EPS block molding process is pre-expansion. This involves expanding the raw polystyrene beads (called expandable polystyrene beads) to many times their original size. The beads contain a small amount of pentane gas, which acts as a blowing agent. During pre-expansion, the beads are exposed to steam within the EPS block machine, causing the pentane gas to vaporize, which results in the beads expanding. The expansion process turns the beads into foam, increasing their volume by up to 40 times.
The degree of expansion is controlled based on the final density required for the EPS block. Lower-density blocks are created by expanding the beads further, while higher-density blocks require less expansion.
Once expanded, the foam beads are allowed to stabilize in a holding area where they cool and reach the desired uniform density before proceeding to the next step.
2. Aging (Stabilization)
After pre-expansion, the expanded beads need to undergo an aging process, which allows them to stabilize and cool down. During aging, air diffuses into the expanded beads, replacing the vaporized blowing agent (pentane). This step is essential because it ensures that the beads have a consistent shape and density, which is critical for the quality and strength of the final EPS blocks.
The aging time can vary depending on factors like the type of beads and their final density, but it typically ranges from a few hours to several days. During this phase, the beads are stored in large silos or hoppers, allowing them to cool naturally and settle.
3. Block Molding
Once the beads are fully stabilized, they are ready for the actual block molding process. This stage takes place in the EPS Block Machine, which is equipped with large molds where the expanded beads are compressed and fused into solid blocks.
The beads are blown into the mold cavity, which is then sealed and subjected to steam once again. The heat from the steam softens the surface of the beads, causing them to bond together. The fusing process is critical to creating a solid block that holds together well without any visible seams or weak points. Steam also helps the beads fill all spaces within the mold uniformly, ensuring that the final block is dense and structurally sound.
The size of the mold determines the size of the block, which can be customized based on industry requirements. Typical block sizes can range from 4×8 feet to larger dimensions, and the thickness of the block can be adjusted as needed.
Once the beads are fused and the block has taken shape, the mold is cooled, and the solidified EPS block is ejected.
4. Curing
After the block has been formed, it needs to undergo a curing process. Curing allows the block to further stabilize and reach its final mechanical properties. During this phase, any remaining moisture from the steam is evaporated, and the block continues to cool down to room temperature.
The curing process is essential because it ensures that the blocks are fully hardened and ready for cutting or further processing. Without adequate curing, the blocks might warp or shrink, which would compromise their structural integrity.
5. Cutting and Shaping
Once cured, the EPS blocks are often cut into smaller sizes or customized shapes to meet specific requirements. EPS block machines are often equipped with cutting tools, such as hot-wire cutters, which allow for precise cutting with minimal material loss. The blocks can be cut into standard-sized sheets for insulation or into specific shapes for packaging or construction purposes.
These cut-to-size EPS sheets or blocks are widely used in the construction industry for thermal insulation in walls, roofs, and floors, as well as in packaging for protecting goods during transport.
Benefits of Using an EPS Block Machine
The EPS block machine is essential for producing high-quality, uniform EPS blocks efficiently. Key benefits of using such a machine include:
- Precision and Consistency: The machine ensures that the expansion, molding, and curing processes are carefully controlled, resulting in consistent block quality.
- Customizable Block Sizes: The EPS block machine allows for flexible block dimensions to suit different industry needs.
- Efficiency: With automated systems, EPS block machines can produce blocks quickly and in large quantities, reducing production times.
- Energy Efficiency: Many modern EPS block machines are designed to minimize energy consumption, using advanced steam management and recycling systems.
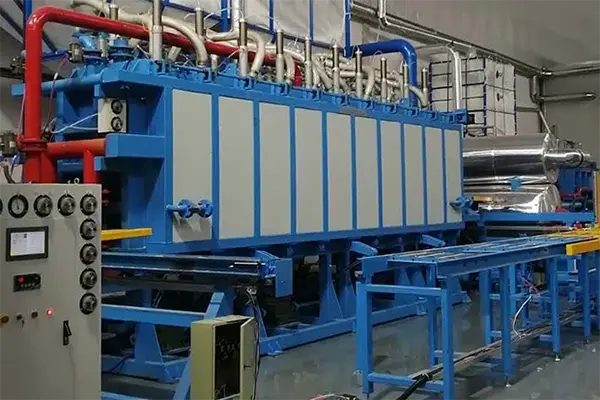

Conclusion
The EPS block molding process involves several critical stages, from the pre-expansion of polystyrene beads to molding, curing, and final cutting. The EPS block machine plays a pivotal role in every step, ensuring that the blocks are strong, uniform, and ready for use in various industries. Whether for construction insulation or protective packaging, the EPS block molding process allows for the efficient and cost-effective production of versatile foam blocks that meet the needs of multiple applications.
Post time: 10-24-2024