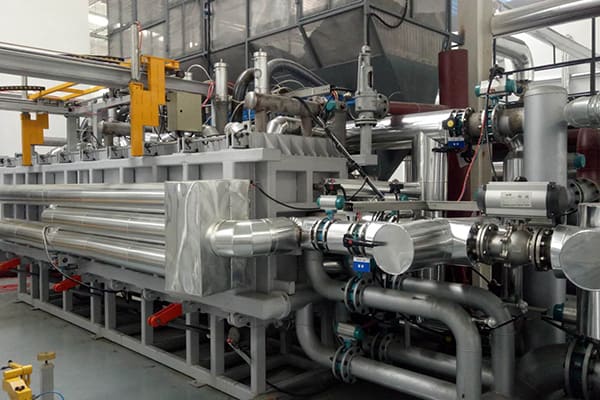
In the realm of industrial manufacturing and packaging, the EPS machine plays a crucial role. EPS stands for Expanded Polystyrene, a versatile plastic material used widely in various applications due to its lightweight and insulating properties. The EPS machine is the specialized equipment used to produce EPS products, and it includes several stages of operations from raw material processing to the final product. This article delves into an EPS machine, its components, how it works, and its applications in different industries.
Components of an EPS Machine
An EPS machine comprises several key components, each performing a specific function in the production process. The primary parts include:
- Pre-expander: This is the initial stage of the EPS production process where polystyrene beads are heated with steam to expand them. The beads contain a blowing agent, usually pentane, which causes them to expand up to 40 times their original size. The pre-expanded beads are then stored in silos for aging and stabilization.
- Block Molding Machine: The beads are transferred to a block molding machine after pre-expansion. Here, the beads are further heated with steam in a mold, causing them to expand further and fuse into a solid block. The mold is then cooled, and the block of EPS is ejected.
- Shape Molding Machine: For products that require specific shapes, the shape molding machine is used. It functions similarly to the block molding machine but is designed to produce custom shapes and sizes based on the molds used.
- Cutting Machine: Once the EPS blocks or shapes are formed, they are often cut into precise dimensions using a cutting machine. These machines use hot wires or blades to slice through the EPS, ensuring accurate and smooth cuts.
- Recycling System: Any excess or waste EPS material is collected and recycled back into the production process. This system ensures minimal waste and maximizes the efficiency of raw material usage.
How an EPS Machine Works
The operation of an EPS machine can be broken down into several steps:
- Pre-expansion: The raw polystyrene beads are fed into the pre-expander, where they are heated with steam. The heat causes the beads to expand and form a cellular structure, increasing their volume significantly.
- Aging: The expanded beads are then stored in aging silos for a period, allowing them to stabilize and release any remaining blowing agent. This process is essential to ensure the beads are ready for molding.
- Molding: The stabilized beads are transferred to either a block molding machine or a shape molding machine. In the mold, the beads are subjected to another round of steam heating, causing them to expand further and fuse. Once the mold cools, the solid EPS block or shape is removed.
- Cutting and Shaping: The molded EPS blocks or shapes are then cut into the desired sizes and shapes using a cutting machine. This step ensures the products meet specific dimensions and design requirements.
- Recycling: Any leftover material from the cutting process is collected and processed through a recycling system. The recycled material is then reintroduced into the production cycle, enhancing the operation’s sustainability.
Applications of EPS Machines
EPS machines are utilized in various industries due to the versatile nature of EPS products. Some common applications include:
- Packaging: EPS is widely used for protective packaging of fragile items due to its cushioning properties.
- Construction: EPS is used in building insulation, lightweight concrete, and structural panels because of its thermal insulation and lightweight characteristics.
- Food Industry: EPS is used to make disposable cups, plates, and food containers as it is hygienic and insulates hot and cold foods well.
- Crafts and Decorations: EPS is easy to cut and shape, making it ideal for crafting and decorative purposes.
Environmental Considerations
While EPS offers numerous benefits, its environmental impact has been a topic of concern. EPS is not biodegradable and can contribute to environmental pollution if not properly managed. However, advancements in recycling technologies are helping to mitigate these issues. Modern EPS machines often include recycling systems that reprocess waste EPS, reducing the environmental footprint of EPS production.
Conclusion
EPS machines are integral to the production of Expanded Polystyrene, a material with widespread applications in packaging, construction, and various other industries. By automating and optimizing the processes of pre-expansion, molding, cutting, and recycling, these machines ensure efficient and high-quality production of EPS products. As technology advances, EPS machines continue to evolve, enhancing their capabilities and sustainability.
Post time: 08-01-2024